SMB Guide to Security: IT Integration and Business Continuity

Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) must integrate IT and Business Continuity. This combination of technology and operational resilience strengthens your organization’s ability to handle disruptions.
Why Integration Matters
- Ensures that critical IT systems support ongoing operations during crises.
- Protects sensitive data while maintaining service availability.
Challenges SMBs Face
- Limited resources: Many SMBs struggle with budgeting for comprehensive business continuity plans.
- Lack of awareness: Over 50% of businesses lacked a BCP in 2020, exposing them to severe risks.
- Cybersecurity threats: Ransomware and other cyberattacks pose risks to operational stability.
What This Guide Offers
We aim to equip you with knowledge for establishing effective business continuity strategies. Below, you’ll gain insights into addressing supply chain disruptions and natural disasters while integrating IT into your BCP.
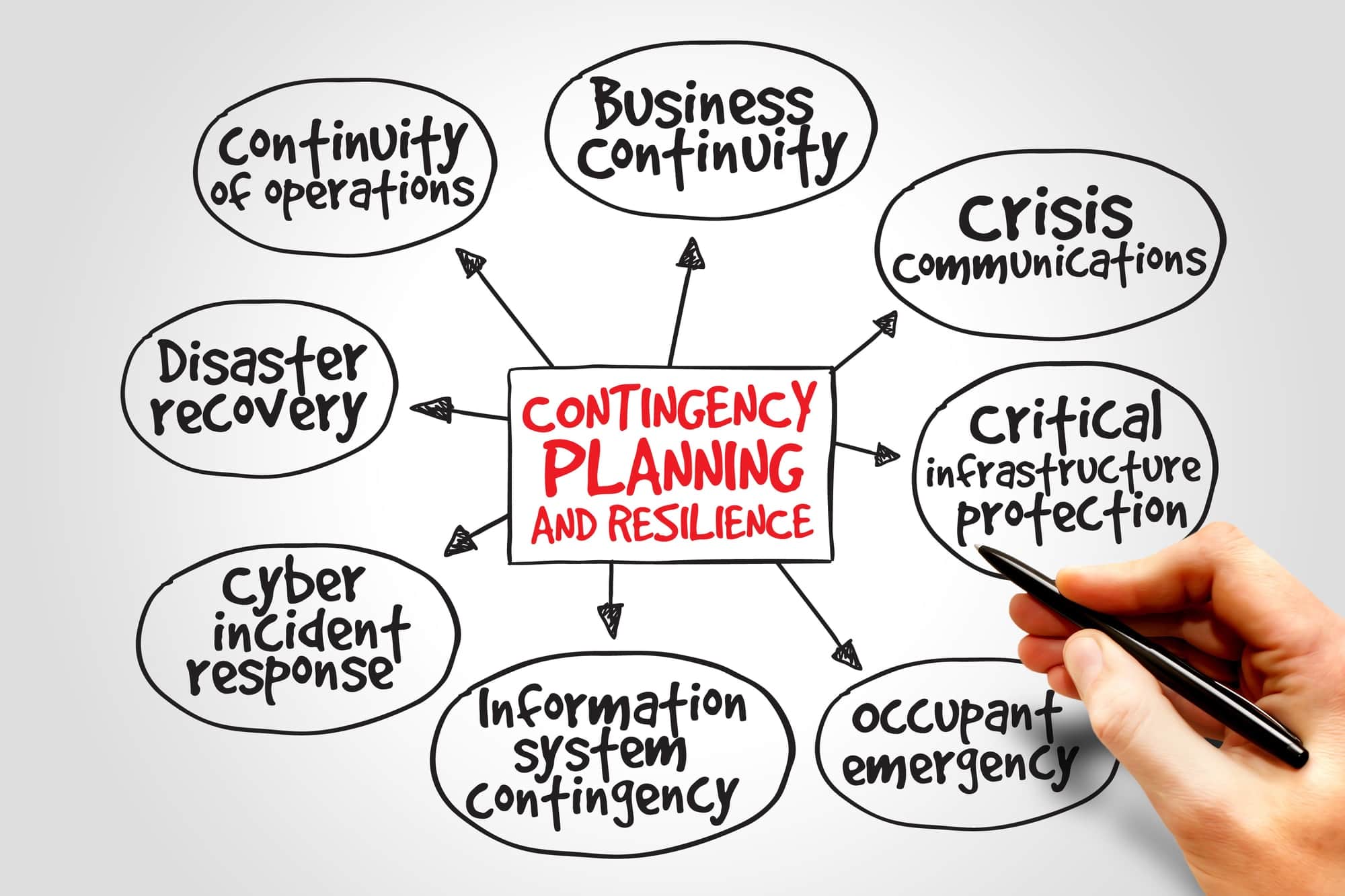
What is a Business Continuity Plan
A Business Continuity Plan (BCP) is a strategic framework that outlines how an organization will continue to function during and after a disruption. It encompasses several critical components:
- Emergency Steps: Procedures to follow during various crises.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Clear assignments of tasks to ensure accountability.
- Communication Protocols: Defined channels for internal and external communication.
- Risk Assessment: Identification and evaluation of potential risks that may impact operations.
The importance of having a BCP extends beyond mere compliance. Every business, regardless of size or industry, stands to benefit from a well-thought-out plan. Reasons include:
- Enhanced Organizational Awareness: Employees understand their roles during emergencies.
- Minimized Financial Risks: Preparedness reduces the financial impact of disruptions.
- Improved Stakeholder Confidence: Customers and partners feel secure knowing your business can withstand crises.
Key elements like communication protocols and risk assessments are essential for effective execution. A BCP should be accessible to all staff, ensuring that everyone is prepared and informed in times of uncertainty. This foundation sets the stage for more complex planning strategies that follow.
Differences Between BCP and Disaster Recovery Plan
- Business Continuity Plan (BCP): Focuses on maintaining ongoing operations during a crisis. Its primary goal is to ensure that critical business functions continue without disruption.
- Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP): Concentrates on restoring systems and data after a disaster has occurred. The emphasis is on recovery to normal operations.
Scenarios
- BCP Example: A retail store implements a plan to keep operations running during a crisis, including remote customer service options and online sales.
- DRP Example: A company experiences a data breach and uses its DRP to recover lost data, restore affected systems, and IT infrastructure stays online.
Benefits of Business Continuity Planning
1. Organizational Awareness
A well-defined BCP enhances understanding across all levels of the company. Employees become familiar with their roles, responsibilities, and the protocols during a crisis. This increased awareness promotes a culture of preparedness.
2. Financial Risk Reduction
A proactive approach to business continuity minimizes potential financial losses during disruptions. By identifying critical functions and resources, you can allocate budgets more effectively, reducing unexpected expenses linked to crises.
3. Improved Employee Relations and Customer Satisfaction
When employees feel secure and know their roles, it fosters a positive workplace environment. Satisfied employees lead to better customer interactions, ultimately enhancing client loyalty. Customers appreciate knowing that your business is prepared for unforeseen events, further solidifying their trust in your brand.
Crisis Management and Emergency Preparedness in IT and Business Continuity Planning
Crisis management is vital for SMBs to navigate unexpected disruptions. Effective strategies include:
- Establishing a Response Team: Designate a team responsible for crisis management, keep this team familiar with the BCP.
- Regular Training and Drills: Conduct simulations and drills to prepare staff for various crisis scenarios, enhancing their readiness and confidence.
- Clear Communication Channels: Develop protocols for internal and external communication during a crisis, ensuring timely updates to employees, stakeholders, and customers.
Emergency preparedness plays a pivotal role in maintaining operations.
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential threats specific to your business environment. This helps prioritize resources effectively.
- Resource Allocation: Ensure that critical resources, such as data backups and IT equipment, are readily available.
- Contingency Plans: Create backup plans for various operational aspects. This may include alternative supply chain options or remote work arrangements.
Risk Assessment Strategies: Identifying Financial Risks and Mitigating Cybersecurity Threats in IT and Business Continuity Planning
Conducting thorough risk assessments is a critical component of IT and business continuity planning. Identifying potential threats helps organizations prepare for disruptions that could impact operations. Key aspects of financial risks identification include:
- Operational Downtime: Loss of revenue due to halted operations.
- Supply Chain Interruptions: Increased costs from sourcing alternative suppliers.
- Regulatory Fines: Financial penalties for non-compliance during crises.
Cybersecurity threats also pose significant challenges. Common threats include:
- Ransomware: Malicious software that encrypts data, demanding payment for decryption.
- Malware: Harmful software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to systems.
To mitigate these cybersecurity risks effectively, consider implementing best practices such as:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra layer of security beyond just passwords.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Protects data transmission over the internet by encrypting connections.
- Data Encryption: Ensures sensitive information remains unreadable without proper decryption keys.
Building Resilience in Your SMB Through Integrated IT and Business Continuity Planning
Building resilience in your SMB requires a proactive approach to integrated IT and business continuity planning. Consider these actionable steps:
- Develop a Comprehensive BCP: Ensure your plan encompasses both IT-related risks and other potential disruptions.
- Engage Your Team: Involve staff in the planning process to enhance awareness and effectiveness.
- Regularly Update Your Plans: Keep your BCP current with changing business needs and emerging threats.
The significance of integrating IT with business continuity cannot be understated. A cohesive strategy not only safeguards operations during crises but also fosters long-term success. Take the necessary steps today to secure your business’s future.
Frequently Asked Questions About Business Continuity
What is a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) and why is it important for SMBs?
A Business Continuity Plan (BCP) is a strategic framework that outlines how a business will continue operating during and after a disruption. For small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), having a BCP is crucial as it minimizes downtime and protects vital resources. Key components include communication protocols, risk assessments, and recovery strategies.
How does a Business Continuity Plan differ from a Disaster Recovery Plan?
While both plans are essential for managing disruptions, they serve different purposes. A Business Continuity Plan (BCP) focuses on maintaining ongoing operations during crises, whereas a Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) specifically addresses the recovery of IT systems and data post-disaster.
What are the key benefits of implementing Business Continuity Planning?
Implementing Business Continuity Planning offers several benefits, including enhanced organizational awareness, reduced financial risks, improved employee relations, and increased customer satisfaction. By preparing for potential disruptions, businesses can maintain operational continuity and foster trust among stakeholders.
What strategies should be used for effective crisis management in IT and business continuity planning?
Effective crisis management strategies include developing clear communication channels, conducting regular training exercises, and creating detailed emergency response plans. It’s essential to prepare staff for potential disruptions to ensure smooth operations during crises and maintain business continuity.